A new lidar (“Laser Imaging Detection and Ranging”) at the Santa Cruz de Tenerife Observatory of the Izaña Atmospheric Research Centre will allow us to analyze the vertical structure of the Saharan air layer and the marine boundary layer more precisely
![]()

The Izaña Atmospheric Research Centre has acquired a new lidar, namely CE376, from Cimel Electronique, which works at two wavelengths (532 & 808nm) with 2 depolarization channels.
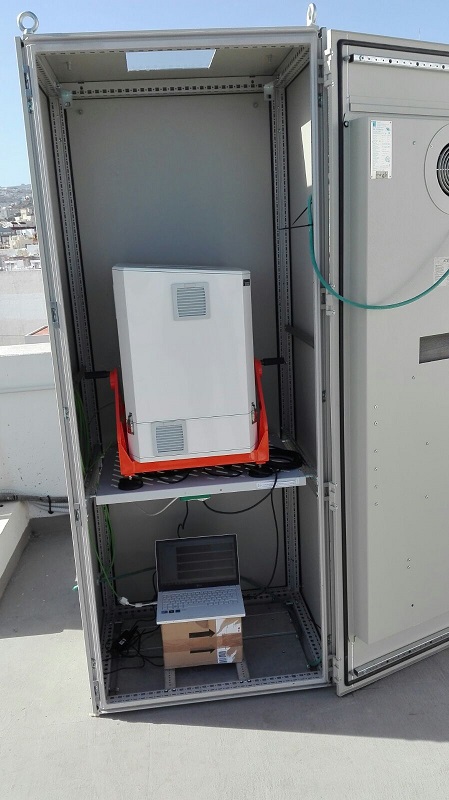

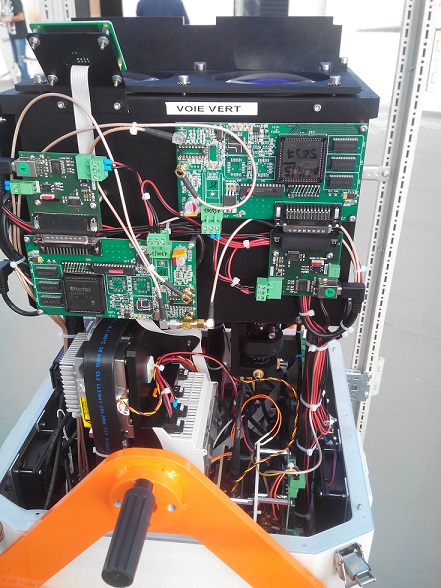
The new Cimel CE376 lidar in the thermostatized enclosure on the terrace of the Santa Cruz Observatory (Izaña Atmospheric Research Centre) and different details of the instrument.
This lidar has been purchased as part of the project “Equipment for greenhouse gases and aerosols monitoring and research at the Izaña Global Atmospheric Watch observatory”, financed by the Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (MINECO) of Spain (specific competitive call for research infrastructures). The project is supported (80%) by MINECO using European Regional Development Funds (ERDF), and (20%) by the State Meteorological Agency of Spain (AEMET).
This lidar will be part of the Global Atmosphere Watch program, and will be a key element complementing current column aerosols optical properties programmes such as AERONET (Aerosol, RObotic NETwork; http://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov) programme at Santa Cruz de Tenerife and Izaña stations, and GAW-Precission Filter Radiometer programme at Izaña station. The lidar will also provide near real time data for evaluating dust models at the “Sand and Dust Storm Warning Advisory and Assessment System” Regional Center for Northern Africa, the Middle East and Europe (http://SDS-WAS.aemet.es/), coordinated by AEMET, and managed by AEMET and the National Supercomputing Center (BSC-CNS).