Reactive gases monitoring program at Izaña
REACTIVE GASES MONITORING PROGRAM AT IZAÑA ATMOSPHERIC RESEARCH CENTRE
Visitors for reactive gases studies
Pictures
Objective
The objective is to perform a continuous monitoring of reactive gases related to climate forcing and air quality on multi-decadal time scales in the subtropical North Atlantic free troposphere. For this purpose, ozone, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides are monitored in a continuous basis. This project is being developed within the framework of the Global Atmospheric Watch Program of the World Meteorological Organization.
Measurements
INLETS
Two inlets are use for reactive gases measurements. One is used for collecting ozone samples and the other is used for collecting carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. Vertical laminar flow manifolds are used to take the sample air assuring residence times of the air masses less than 10 seconds.


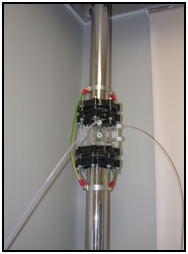
Fig. 1. Inlets and an example of the vertical laminar flow manifolds of reactive gases at Izaña.
ZERO CHECKS AND CALIBRATIONS
Zero checks are made during 15 minutes in a daily period. In the case of carbon monoxide, this zero check is carried out each half an hour to minimize the influence of temperature fluctuations.
Multipoint calibrations are made each three months. A primary standard 49C-PS is used to calibrate the ozone analyzers, while a dilution system with cylinders is used to calibrate the rest of compounds. In addiction a GPT system is used to calibrate NO2 measurements.


Fig. 2. Scrubbers of the 43C, 48C ad 42C models, respectively.
INSTRUMENTS
The methodologies used by these analyzers have been declared as reference methods by the Environmental Protection Agency of USA and the European Union.
| Parameters |
Instrument pictures |
| Ozone concentration is measured by UV Photometric absorption. Model 49C (Thermo Electron Corporation). |
 |
|
Carbon monoxide is measured by a gas filter correlation analyzer. |
 |
| Sulphur Dioxide is measured by pulsed fluorescence analyzer. Model 43C-TL (Thermo Electron Corporation). |
 |
| Nitrogen oxides are measured by a chemiluminescence technique. The molybdenum converter has been replaced by a photolytic converter to minimize nitrogen species interferences. Model 42C-TL (Thermo Electron Corporation). |
 |
More details on the measurements are provided at GAWSIS
Research
Reactive gases at Izaña Observatory are focused on the characterization of these gases in the free troposphere, its trends, the analysis and detection of the long range transport mechanism and its influence as precursors of nanoparticles formation.
The characterization of reactive gases in the free troposphere
A minimum in summer and autumn time (≈70 ppb) and maximum in winter and spring (≈140 ppb) are observed for CO measurements:
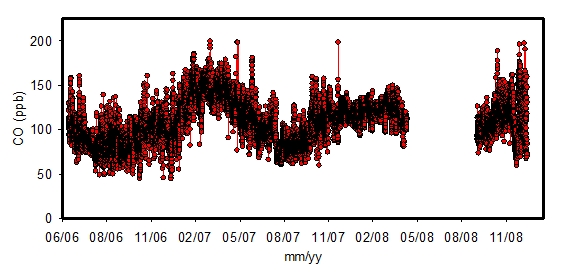
Fig. 3. Time series of carbon monoxide (2006-2008).
At Izaña station a trace level analyzer for nitrogen oxides measurements with a molybdenum converter was installed in a first stage. Molybdenum converters are non specific for determination of nitrogen dioxide (NO2), because their response to other nitrogen-containing compounds as peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) and a variety of other organic nitrates and nitric acid, which provokes an overestimation of NO2 measurement, specially, when sampling photochemically aged air masses or in remote locations, where NOx is small compared with NOy (Winer et al., 1974, Steinbacher et al., 2007). Because of this, the output was understood as a good approximation of the total gas phase “nitrogen oxides” (NOy). In a second stage, the molybdenum converter was replaced by a photolytic one which uses ultraviolet light, which allows a better measurement of NO2 in this location.
Nitrogen oxides do not reveal a seasonal pattern, which is explained by the conjunction of opposite processes: the thermally induced vertical transport and the chemical lifetime of NOx (Zani et al., 2007). SO2 does not present a seasonal pattern too.
The upward orographic flows provoke the transport of polluted boundary layer air to the height of Izaña in a daily cycle between 10h to 18h. This mixing with the boundary layer air provokes an increase of NOX mixing ratios and SO2, and a decrease in O3 mixing ratios.
Out of this time period, we could expect to measure the representative troposphere levels in the tropical region of reactive gases, unfortunately, in the case of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, this estimation is a difficult matter because they remain under the detection limits ( <60pptv and <50 pptv, respectively).
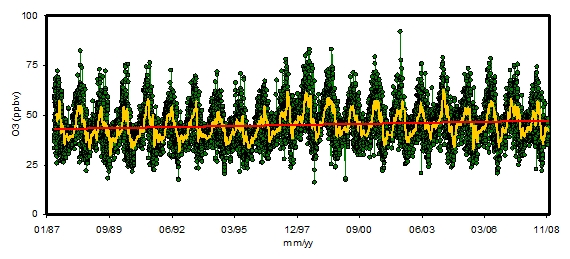
Fig. 4. Time series of surface ozone (1987-2008).
The influence of reactive gases as precursors of nanoparticles formation
New particle formation is observed almost every day in the upward orographic flows that are developed during daylight around Tenerife Island. The transport of water vapour and gaseous precursors due to upward flows from the boundary layer the low free troposphere results on new particles of a few nanometres.
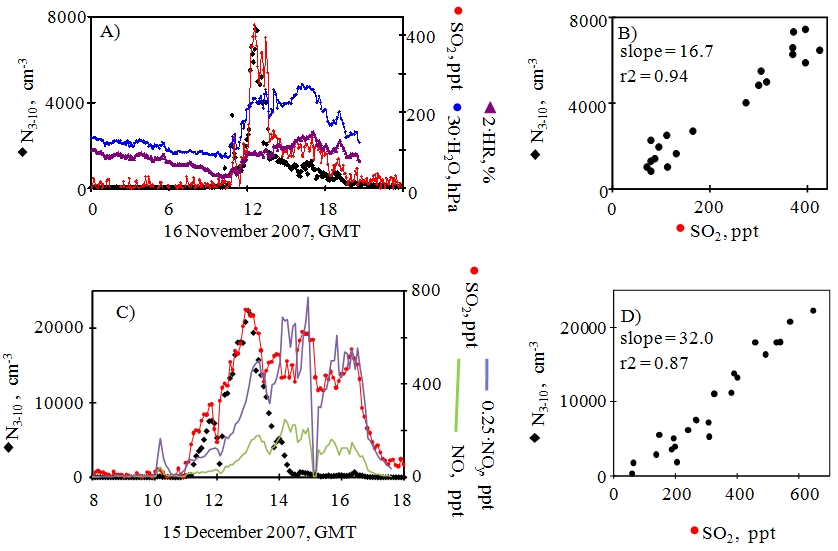
Fig. 5. Five-minutes averaged values of N3-10, SO2, water vapour concentrations and relative humidity during two events (16 November 2007 and 1 October 2007)
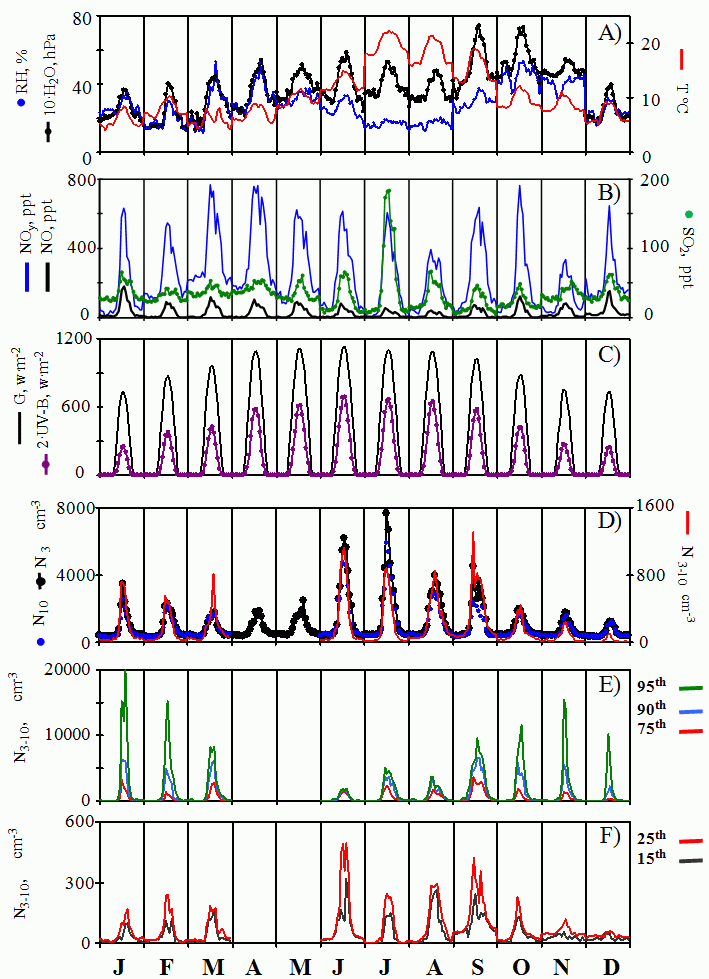
Fig. 6. Hourly median values and percentiles for each month of 2007 of: (A) relative humidity (RH), water vapour (H2O) and temperature (T), (B) SO2 and NOy concentrations, (C) global (G) and UV-B radiation, (D) N10, N3 and N3−10 concentrations, and (E) percentiles 70-th, 90-th and 85-th of N3−10, and (F) percentiles 15-th and 25-th of N3−10.
Dr. Emilio Cuevas Agulló (link to personal page)
Dr. Sergio Rodríguez González (link to personal page)
Ramón Ramos López (link to personal page)
Visitors for reactive gases studies (since 2004)
| Name | Institution | Period |
| Dr. C. Zellweger and Dr. J. Klausen |
Global Atmosphere Watch World Calibration Centre for Surface Ozone Carbon Monoxide and Methane, EMPA |
30/11/2004 – 4/12/2004 |
| María Elena Barlasina |
Ushuaia GAW Station |
01/09/2008 – 01/10/2008 |
| Ricardo Daniel Sánchez | Servicio Meteorológico Nacional de Argentino | 01/09/2008 – 01/10/2008 |
| Dr. C. Zellweger | Global Atmosphere Watch World Calibration Centre for Surface Ozone Carbon Monoxide and Methane, EMPA |
4/03/2009 – 11/03/2009 |
Publications based on reactive gases observations at Izaña
Rodríguez, S., González, Y., Cuevas, E., Ramos, R., Romero, P.M., Abreu-Afonso, J., Redondas, A., Atmospheric nanoparticle observations in the low free troposphere during upward orographic flows at Izaña Mountain Observatory. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions, 9, 10913–10956, 2009. Still in open discussion period !!! (download pdf)