New paper on Saharan Air Layer characterization using ground-based remote sensing techniques
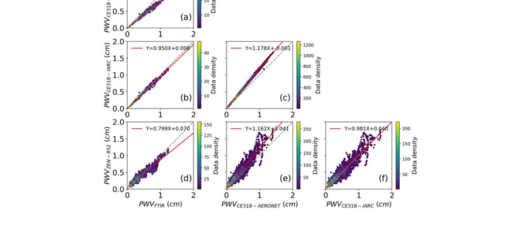
A new paper entitled “Synergetic monitoring of Saharan dust plumes and potential impact on surface: a case study of dust transport from Canary Islands to Iberian Peninsula” by Córdoba et al. has been published in “Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions”. This paper deals a case study of air masses advected from Saharan region to the Canary Islands and the Southern Iberian Peninsula, relatively located close and far away from the dust sources, respectively. The observations were performed over three Spanish geographically strategic within the dust-influenced area stations along a common dust plume pathway: “Santa Cruz de Tenerife Observatory” (SCO-AEMET), the Atmospheric Sounding Station “El Arenosillo” (Huelva, ARN-INTA) and the Granada station (GRA-ULL). Remote sensing both ground-based active (lidar) and passive (sun-photometry) techniques together with backtrajectory analysis and in situ measurements have been used for the characterization of dust intrusions.
Full reference:
Córdoba-Jabonero, C., M. Sorribas, J. L. Guerrero-Rascado, J. A. Adame, Y. Hernández, H. Lyamani, V. Cachorro, M. Gil, L. Alados-Arboledas, E. Cuevas, and B. de la Morena, Synergetic monitoring of Saharan dust plumes and potential impact on surface: a case study of dust transport from Canary Islands to Iberian Peninsula, Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss., 10, 1–60, 2010, doi:10.5194/acpd-10-1-2010.
To download the paper click here
To link the Discussions site click here