NO2 Campaign at Izaña
Henri Diémoz, researcher of the Environmental Agency of Aosta Valley (Italy), will develop a new technique to measure nitrogen dioxide NO2 using the Brewer Spectrophotometer at the Izaña observatory thanks to the RBCC-E (Regional Brewer Calibration Center for Europe) facilities. The Brewer Spectrophotometer is a versatile instrument can measure total column ozone (O3), sulfur dioxide (SO2), spectral Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) on the UV range, as well as ozone vertical profiles. The MKIV Brewer would be potentially of measuring NO2 on the visible range. However this measurement is not reliable, yet. The new algorithm in development uses more wavelengths and new cross sections to try to capture the weak signal of NO2. The calibration of NO2 measurements uses the Langley method which requires pristine sky conditions and stable atmospheric conditions, typical of the Izaña Observatory.
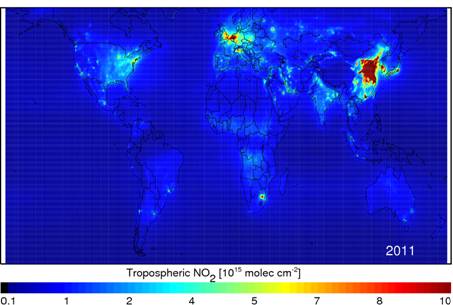
The tropospheric NO2 from OMI satellite during the 2011 (image from http://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/Aura/data-holdings/OMI/omno2_v003.shtml). The most prominent sources of NO2 are internal combustion engines and thermal power stations.
The NO2 is an atmospheric gas playing an important role on the ozone photochemistry in both the stratosphere and the troposphere and is one of the main indicators of the air quality .The NO2 is routinely measured at Izaña since 1991 using a DOAS technique by the cooperation project with the INTA. This measurement will be used to validate this new development. The measurement campaign started last week and will continue until the end of October. The measurements from this technique could be extended to the more than 100 Brewer instruments installed all over the world and help satellite validation.
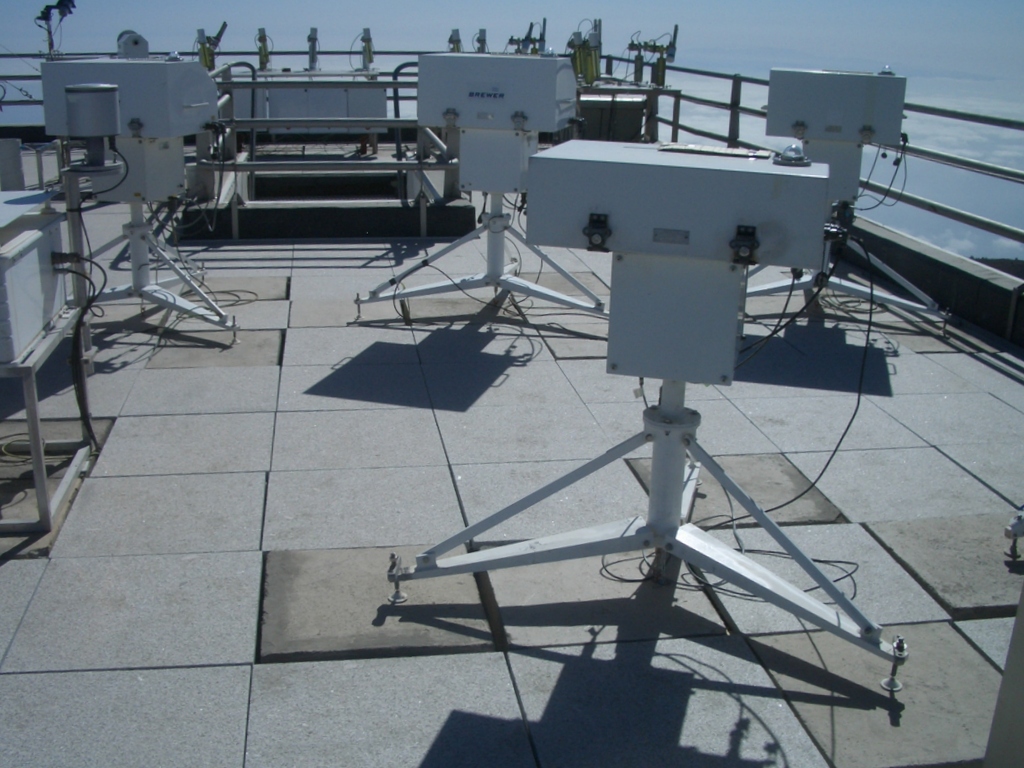

The Brewer photometer #066 from Valle de Aosta-Italy (in the foreground) measuring at Izaña with the RBCC-Brewer reference triad.