New paper in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres: “Solar radiation measurements compared to simulations at the BSRN Izaña station. Mineral dust radiative forcing and efficiency study” by García et al.

The paper entitled “Solar radiation measurements compared to simulations at the BSRN Izaña station. Mineral dust radiative forcing and efficiency study” has been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres.
This paper presents a comparative study of shortwave downward radiation (SDR) measurements and simulations, obtained with the LibRadtran radiative transfer model (RTM), at the Baseline Surface Radiation Network (BSRN) site of Izaña Atmospheric Observatory (IZA, Spain). The analysis is based on cloud-free days between March 2009 and August 2012 (386 days), including aerosol-free and Saharan mostly pure mineral dust conditions and comparing the day-to-day, annual and interannual variability. The observed agreement between simulations and measurements is excellent: the variance of daily measurements overall agrees within 99% with the variance of daily simulations and the mean bias (simulations minus measurements) is -0.30±0.24 MJm-2 for global, -0.16±0.34 MJm-2 for direct and +0.02±0.25 MJm-2 for diffuse SDR.
Furthermore, the diurnally averaged aerosol radiative forcing (∆DF) and radiative forcing efficiency (∆DFeff) due to Saharan mostly pure mineral dust events has been computed at Izaña Observatory. The mean ∆DF values are -7±1, -96±5 and 44±2 Wm-2 for global, direct and diffuse BSRN SDR, respectively (mean aerosol optical depth, AOD, at 500 nm of 0.18±0.01), while the mean ∆DFeff values are – 59±6, -495±11 and 230±8 Wm-2 per unit of AOD at 500 nm for global, direct and diffuse BSRN SDR, respectively (see Figure). This illustrates the significant potential of mineral dust particles to cool the Earth-atmosphere system.
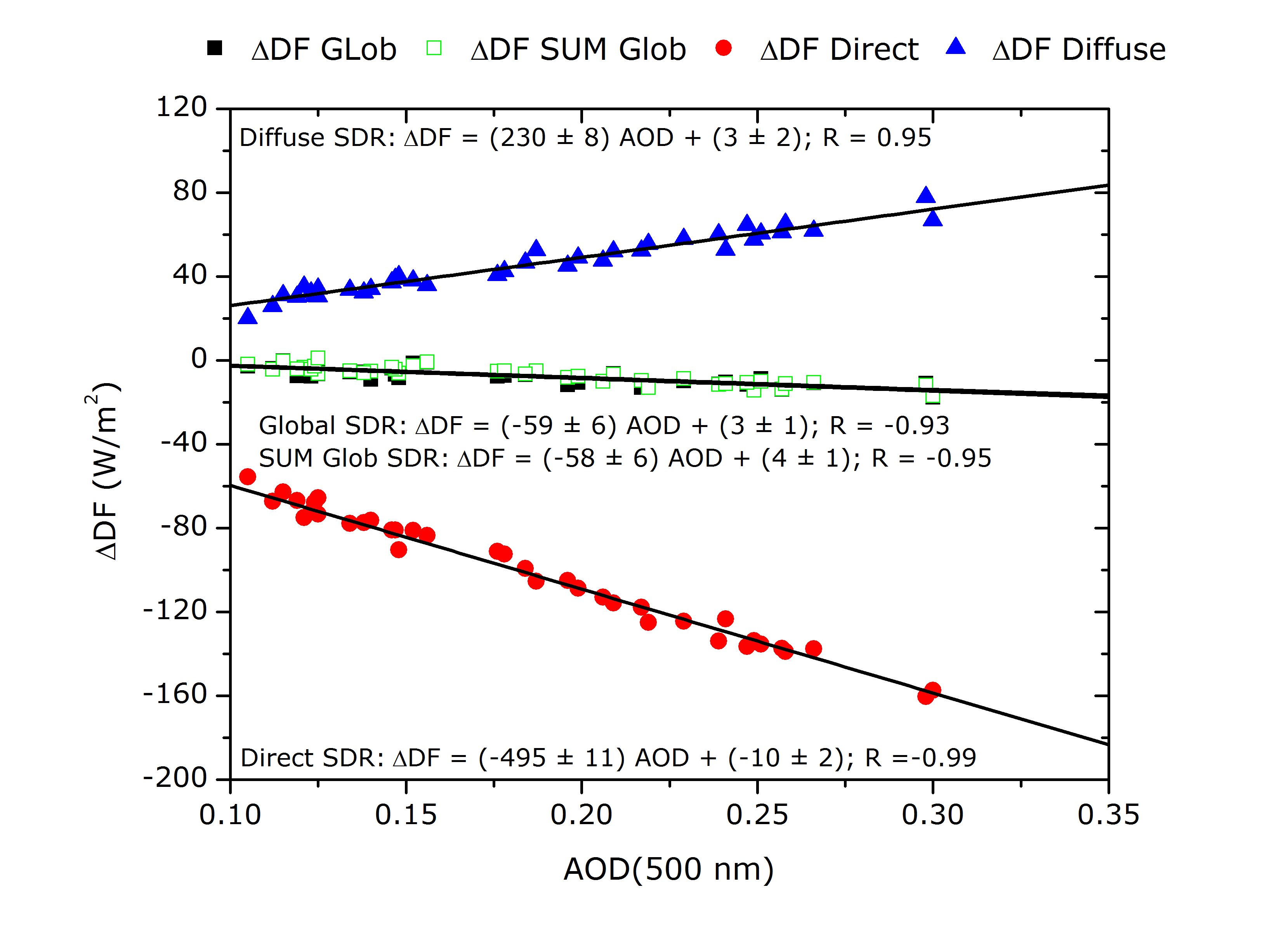
Diurnally averaged aerosol radiative forcing (∆DF) versus the daily averaged AOD at 500 nm for global (black squares), SUM Glob (green squares), direct (red dots) and diffuse SDR (blue triangles) for all cloud-free days with daily averaged AOD>0.10 and α<0.75 from March 2009 to August 2012 at BSRN IZA (N=39 days). The black solid lines are the least square fits, where the slopes represent the diurnally averaged aerosol radiative forcing efficiency (∆DFeff-slope).
The full references is:
García, R.D., O.E, García, E. Cuevas, V.E. Cachorro, P.M. Romero-Campos, R. Ramos and A.M. de Frutos, Solar radiation measurements compared to simulations at the BSRN Izaña station. Mineral dust radiative forcing and efficiency study, JGR-Atmospheres, DOI: 10.1002/2013JD020301.
You can download the paper at:
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2013JD020301/abstract